How Mature is Your Cyber Security Model?

In the previous articles, we’ve been discussing cyber security throughout different angles and perspectives, but we’ve never talked about its maturity model and how it’s important in the modern world. First of all, we should define what the term cyber security means. As it is known, security represents a process of maintaining an acceptable level of risk. So, does that mean that, by the same definition, cyber security is a process of maintaining an acceptable level of cyber risk? Basically, that’s exactly what it does. In this article, we will try to define a cyber security maturity model, explain approaches to cyber operations and introduce some maturity levels. Well, let’s start with our story.
Introduction
At the beginning, we should try to explain why maturity is so important in terms of security or even cyber security. Also, we believe, at this stage, it’s not completely clear what we mean by maturity or its model. So, what do you think a maturity could represent in terms of cyber security? When we say something is mature, what we mean by that? In this case, a cyber security model has a certain level of maturity if it can obtain a high level of its operations in terms of its human recourses, processes and technology. Well, if we wish a high level of maturity of any cyber system, we need it being capable to provide highly controlled and reliable processes, get driven by highly skilled and motivated people and supported with the cutting-edge technology.
Further, what we could mention is that this is not the fact in the real world. In the reality, a lot of enterprises suffer some difficulties and they are not able to obtain a competitive level of cyber maturity. In fact, the reason for that is the world’s lobber market is facing up some sort of crisis if it comes to cyber professionals, so only small percentage of cyber systems can say for themselves that they are mature. Experts believe this gap can be covered only within few decades.
So, what are the challenges that we face up today? Firstly, a modern world has a lack of capable cyber professionals and, consequently, if we do not have experts to manage their tasks, our working process cannot be covered appropriately as well. In other words, developed countries have an advantage if we talk about modern technology, but if there are not enough competitive people to use those technological solutions and to maintain processes through them, the problem must get obvious. The reason why we suffer a cyber skills shortage is that a cyber security career is highly challenging and quite difficult and requires a lot of investment and hard work in order to get ready to contribute on the market.
The Best Approaches to Cyber Operations
As it is known, traditional approaches to Cyber Operations are proving to be inadequate against today’s increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. Too often, governments and businesses find themselves one step behind attackers, reacting to rather than anticipating each new threat. It is obvious that a new approach to Cyber Operations is required, one that is proactive, dynamic, adaptive, and recognizes that cyber security occurs within a cyber ecosystem of multiple, interdependent actors who also are potential partners in combating cyber threats.
That new approach to Cyber Operations builds on principles and practices of other communities to create a response lifecycle that integrates four operational functions:
(1) Anticipation. Understanding existing vulnerabilities and emerging threats to develop proactive contingency plans for responding in network time—seconds and minutes—to a cyber event.
(2) Awareness. Implementing automated systems and processes to provide a complete, accurate, real-time understanding of the health and status of networks.
(3) Action. Initiating response plans to anomalies and attacks by coordinating activities to achieve a unified, dynamic network defence that minimizes the impact and facilitates rapid recovery.
(4) After-Action. Determining what happened, who did it, how they did it, and incorporating the lessons learned to create future plans and responses that are adaptive.
It is critical that organisations develop these essential functions to improve operational effectiveness. Once organisations have internally matured, they can more deeply collaborate externally with others in the cyber ecosystem.
What Do We Mean by Maturity Level?
Let’s start with the maturity levels in the cyber security. Each of the maturity levels in the cyber model have been assigned a name indicative of the types of threats and activities being addressed at the level.
The first level is labelled “Security Aware” which correctly implies that the major theme of activities at this level is to make individuals and organisations aware of the threats, problems, and issues related to cyber security.
The second level is labelled “Process Development” and, again, provides a significant clue as to what the theme of this level is. Level 2 elements are designed to help communities establish and improve upon the security processes required to effectively address cyber security issues.
Level 3 of the model is “Information Enabled” and indicates that organizations within the community are all aware of the issues related to security and have the processes and mechanisms in place to identify security relevant events. The goal at this level is to improve upon the information sharing mechanisms within the community to enable the community to effectively correlate seemingly disparate pieces of information. By doing so, a picture can be provided that might indicate an impending attack.
Level 4 of the model is “Tactics Development”. At this level elements are designed to develop better and more proactive methods to detect and respond to attacks. By this level most prevention methods should be in place.
The top level of the model is “Full Security Operational Capability” and represents those elements that should be in place for any organization to consider itself fully operationally read y to address any type of cyber threat. This does not imply that entities at this level will be free from any successful attack but rather that they have done everything they could in order to prevent and detect attacks.
A Scenario for the Future
A scenario for the future has been given in the Figure 1. As it is shown, a crucially important step of each Cyber Operations approach is its anticipation. It is from vital importance for the cyber system to receive the feedback from all the steps in the line and to return that information to the first step. These can help in better understanding of all the risk and issues in the network.
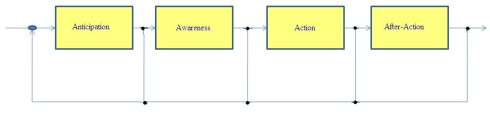
Figure 1. Cyber Operations approach
Conclusions
This article provides a brief overview of cyber security model maturity with some new ideas presented. We believe the information given here are good enough for a basic understanding of the problem.
References:
[1] Booz Allen Hamilton, Cyber Operations Maturity Framework: A Model for Collaborative, Dynamic Cybersecurity, 2011
[2] Gregory B. White, The Community Cyber Security Maturity Model, Proceedings of the 40th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, 2007
Djekic M (2014-07-29 00:15:29). How Mature is Your Cyber Security Model?. Australian Science. Retrieved: Dec 29, 2025, from http://ozscience.com/technology/mature-cyber-security-model/
 Follow
Follow